Changes Around Us for Class 6
Changes Around Us: Introduction
Changes are around us - nature is always changing. Some changes happen slowly, like how trees grow or mountains form. Other changes happen quickly, like after a storm or when animals move. These changes happen because of the weather, animals, plants, and humans. All these changes help nature grow and stay balanced. Understanding these changes helps us appreciate the world around us.
Why do changes happen?
Changes happen in nature for many reasons. The weather, like rain or wind, can change how plants grow. Animals can also cause changes, like when they spread seeds. Sometimes, humans cause changes by building things or cutting down trees. Some changes happen slowly, like mountains forming over many years, while others happen quickly, like after a storm. All these changes help nature grow and change.
Changes can be caused by the following:
|
Change Observed |
Example |
Cause of Change |
|
Melting chocolate |
Chocolate melts when heated |
Change in temperature |
|
Dissolving honey |
Honey mixed with water |
Mixing of substances |
|
Squeezing toothpaste |
Toothpaste comes out of the tube |
Application of pressure |
|
Aging in humans |
Humans grow older |
Biological processes |
Types of Changes
There are several types of changes that can happen:
-
Reversible Changes: Changes that can be reversed. Concrete works the same way; Water vapor can become water, and melting ice can refreeze.
-
Permanent Changes: These changes are irreversible. For example, baking a cake can never return to its ingredients.
-
Physical Changes: Changes that do not change the chemical make-up of a substance (example: Water is heated to steam).
- Chemical Changes: Changes that form new substances (example: Rusting of iron).
Reversible Change:
A reversible change is when the original substance can be retrieved. For instance, an ice cube melts and becomes water and can freeze again to form back into the ice.
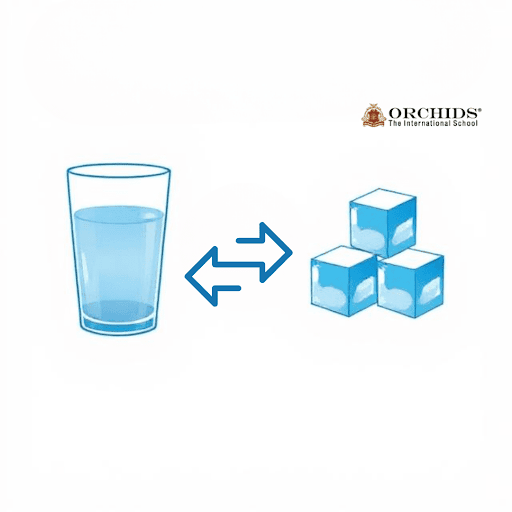
Characteristics of Reversible Changes
-
Temporary in nature.
-
No new substances are formed
Irreversible Change
In an irreversible change new substances are formed that cannot be returned to their original state. For instance, when a wood burns, it creates ash.
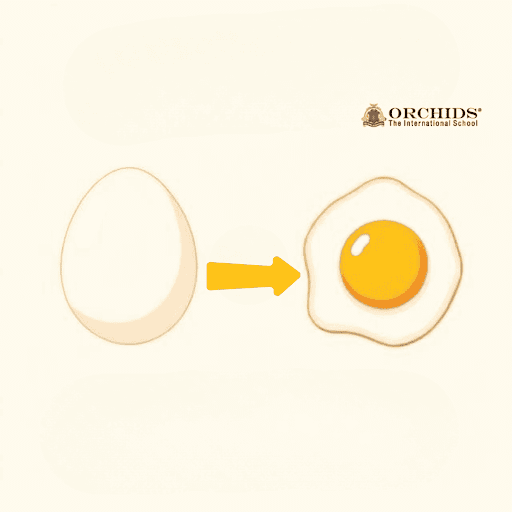
Characteristics of Irreversible Changes
-
Permanent in nature.
-
New substances are formed.
Fun Fact
There is irreversible change when you bake bread—you can’t unflour the bread!
Physical and Chemical Changes
What Are Physical Changes?
State changes are changes that do not affect a substance's chemical composition. Other examples are shape or state changes (melting, freezing, etc.).
Characteristics of Physical Changes:
- No new substances are formed.
- Usually temporary.
Example: An ice cube melts and becomes water and can freeze again to form back into ice.
What Are Chemical Changes?
Chemical change is a process that involves one or more substances being transformed into new substances.
Characteristics of Chemical Changes
- New substances are created.
- Often irreversible.
Example: When you add baking soda to vinegar, a chemical reaction takes place, and carbon dioxide gas is produced.
Environmental Changes, Global Warming, and Climate Change
Our environment encompasses all things around us—such as air, water, land, plants, and animals. With time, the environment may naturally change, but humans have also led to major changes, particularly in the climate.
Climate change is when the Earth's normal weather patterns are altering. Some areas are warming up, some are receiving more rain or heavier storms. Global warming is one of the largest reasons for climate change, and global warming is when the Earth is gradually warming up.

What makes the Earth warm up?
When individuals burn fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and gas (for cars, industry, and power), they emit gases such as carbon dioxide (CO₂) into the atmosphere. Greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, trap sunlight, heating the Earth—like a huge blanket.
Ice at the poles is melting, sea levels are rising, and animals are losing their habitats due to global warming. Global warming also impacts agriculture, water resources, and climate.
How can we assist?
We can conserve energy, recycle, reforest, and employ clean energy such as solar or wind power. Even little things—such as turning off lights or walking to school—can help.
Things you have learned!
-
Change in Nature: Nature changes all the time, from slow changes like tree growth to quick ones like storms.
-
Why Changes Happen: Changes happen due to weather, animals, plants, and humans.
-
Types of Changes: There are physical changes (no new substances) and chemical changes (new substances are formed).
-
Examples of Changes:
-
Melting (Physical): Chocolate melts when heated.
-
Dissolving (Physical): Honey mixes with water.
-
Squeezing (Physical): Toothpaste comes out of the tube.
-
Aging (Chemical): Humans grow older.
-
CBSE Schools In Popular Cities
- CBSE Schools in Bangalore
- CBSE Schools in Mumbai
- CBSE Schools in Pune
- CBSE Schools in Hyderabad
- CBSE Schools in Chennai
- CBSE Schools in Gurgaon
- CBSE Schools in Kolkata
- CBSE Schools in Indore
- CBSE Schools in Sonipat
- CBSE Schools in Delhi
- CBSE Schools in Rohtak
- CBSE Schools in Bhopal
- CBSE Schools in Aurangabad
- CBSE Schools in Jabalpur
- CBSE Schools in Jaipur
- CBSE Schools in Jodhpur
- CBSE Schools in Nagpur
- CBSE Schools in Ahmednagar
- CBSE School In Tumkur











