Light: Reflection
What is Reflection of Light?
When light hits an object, some of it is reflected off ( light bounce off the surface rather than passing through it). Similar to when you look at your face in a mirror, it is light being reflected off of you from the mirror! Here are additionally other surfaces that causes reflection, like when you look into water, shiny metals & glass or ice with cleansed surface. To start, light travels in straight lines, and when it hits a surface, it reflects. Such phenomenon is called reflection of light.
The Law of Reflection
While discussing with the reflection of light, it is necessary to mention the law of reflection! It’s pretty simple:
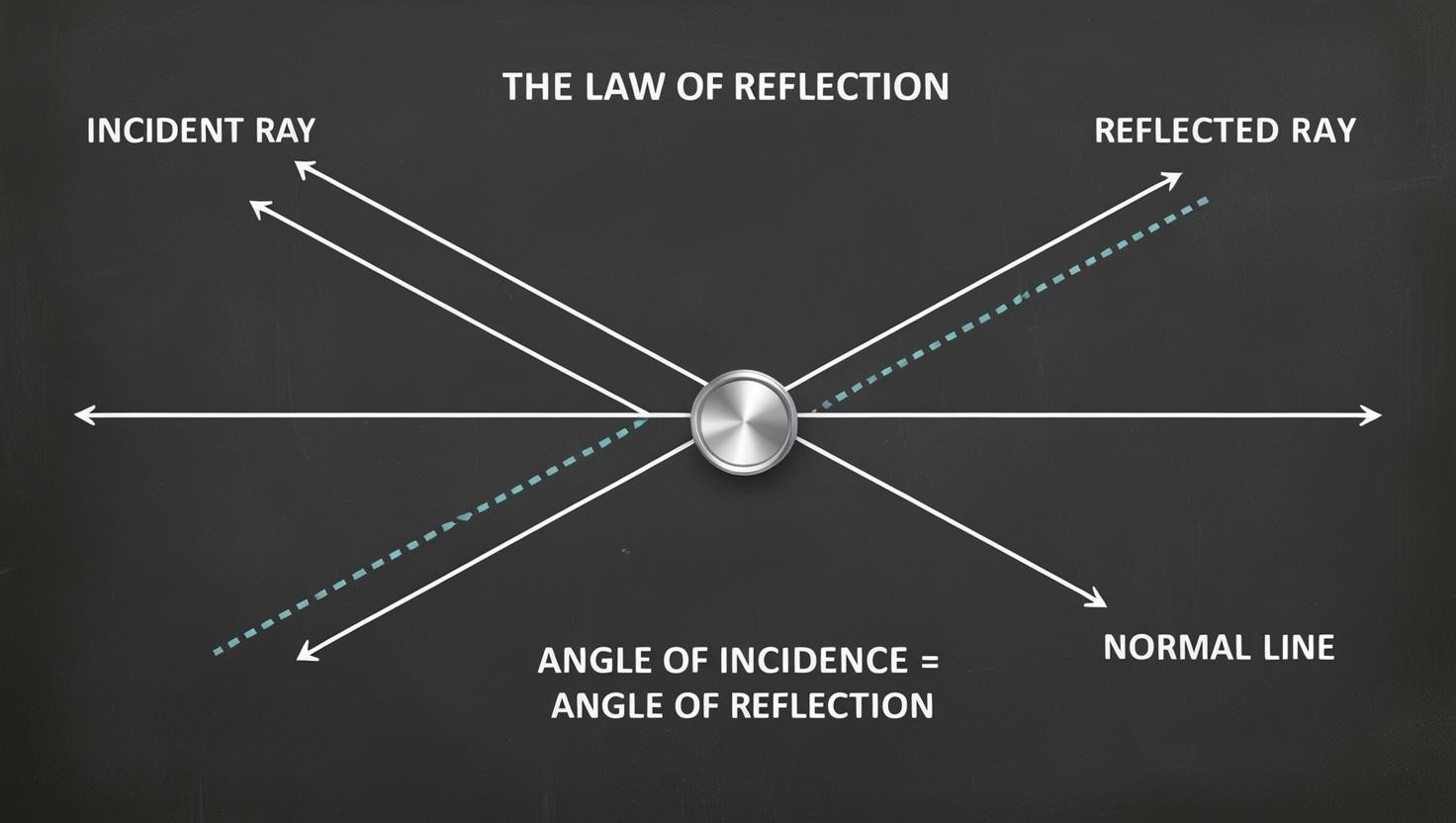
-
When sound waves hit the surface, the angle it strikes (Angle of incidence) is same as the angle it bounces out (Angle of reflection).
-
So, incident ray, reflected ray and one more thing — this is normal (it is an imaginary line drawn perpendicular to the surface surface) — all of them lie in the same plane.
Which pretty much means that light bounces off at the angle that it hits.
Reflection in Everyday Life
Reflection isn’t only a science experiment that you conduct at school – it factors into everything you do!
- Mirrors: A light mirror reflects the light on it and we see our image.
- Lakes and Pools: On calm days, the water reflects trees, mountains, even the sky, in stunning tableaux.
- Shiny Surfaces: Have you ever looked at your phone screen & find how much light it reflects? Example of the reflection of light, that's another.
Different Surfaces and Reflection
Different surfaces can reflect light in a different manner. How smooth or how rough they are!
- Smooth Surfaces (like mirrors): They reflect light in a clear & defined manner, resulting in sharp images. This is known as regular reflection.
- Rough Surfaces (like a wall): A light incident on them scatters it in multiple directions & no clear image is formed. This is diffuse reflection.
So the next time you look at your phone screen or see your reflection on a calm lake, you’re seeing the effect of smooth surface light reflection in action!

What is a Reflection of Light on the pH Scale?
Conduct Reflection — To Explain Something Moving(Weird connection here with the pH scale) You might be wondering how acids, bases and pH relate to light — but bear with us — it’s a fascinating track!
Acids, bases, and pH are all about measuring how acidic or basic something is. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14:
- Pure water is neutral (pH 7).
- A pH less than 7 is acidic (such as lemon juice or HCl — hydrochloric acid).
- pH greater than 7 – basic (soap, salts, etc.).
After all, just like light refractors, pH helps us measure how different things react with things around them. Similar to how light bouncing off a surface reflects it, high & low pH substances can shape light in different manners.
In fact, we can see how acidic or basic something is by the way that certain substances change the color of other substances called indicators. Indicators, such as litmus paper, are used for this test, and they show a color change depending on the pH value.
Fun Experiment: Reflection and pH Together!
Imagine if you could work with reflection of light as well as the pH scale? Here’s a fun idea!
Materials Needed:
- Shiny surface (mirror)
- A glass container of water that is clear
- Some HCl (Hydrochloric acid) or vinegar (weak acid)
- Litmus paper or pH indicators strips to determine acidity
Steps:
- Look at how light is reflected on a smooth surface like a mirror.
- Mix some HCl (or vinegar) to the water and test with a pH indicator.
- Refer to the pH which changes the color of indicator.
- Notice how light reflects off the water & the acidic solution.
Real-Life Reflection of Light
Other cool examples of light reflection in the real world:
- Moon Reflection : The moon does not produce light itself — it reflects sunlight! This is one of the great acts of natural reflection.
- Lakes and Puddles: On a rainy day, puddles mirror streetlights, architecture & also the sky, forming gorgeous scenes.
- Mirrors in Cars: Reflective surfaces play an important role in cars, helping drivers to see what is behind them by reflecting light off special surfaces.
Fun Facts About Reflection of Light
- Reflection makes images: When light bounces off a mirror, it produces a reflection that creates an image of whatever’s in front of the mirror.
- You can't see light directly: We see things because light is reflected from those things.
- Reflection helps you see things: Without it, there would only be complete darkness & we wouldn’t see anyone around us.
Key Points to Remember:
- Reflection: The return of a ray of light upon striking a surface.
- There hurl light can be perceived to ricochet off of a surface, similar to a mirror reflection, or a polish to a vehicle.
- The angle at which light hits a surface, known as the angle of incidence, is important when light strikes the surface.
Conclusion
- Reflection of light means light bounces off surfaces and lets us see objects around us.
- We see reflections in mirrors, on water surfaces like lakes, or even the moonlight.
- Reflection helps us perceive and understand the world visually.
- Everyday examples of reflection include mirrors, shiny objects, and calm water surfaces.
- Understanding reflection helps us appreciate how light behaves in our environment.
CBSE Schools In Popular Cities
- CBSE Schools in Bangalore
- CBSE Schools in Mumbai
- CBSE Schools in Pune
- CBSE Schools in Hyderabad
- CBSE Schools in Chennai
- CBSE Schools in Gurgaon
- CBSE Schools in Kolkata
- CBSE Schools in Indore
- CBSE Schools in Sonipat
- CBSE Schools in Delhi
- CBSE Schools in Rohtak
- CBSE Schools in Bhopal
- CBSE Schools in Aurangabad
- CBSE Schools in Jabalpur
- CBSE Schools in Jaipur
- CBSE Schools in Jodhpur
- CBSE Schools in Nagpur
- CBSE Schools in Ahmednagar
- CBSE School In Tumkur











