Multiplication
Introduction: Multiplication
Multiplication is a process of combining groups of equal size. It is one of the fundamental arithmetic operations in mathematics. This operation has been used from ancient times in the name of “Gunana”, meaning multiplication, which is found in Vedic maths. Brahmaguptha was the first Indian mathematician who discover multiplication in India. Let us understand the concept of multiplication, symbol representation, times tables up to 20 and solve some problems.
Table of Contents
- What is Multiplication?
- Multiplication Symbol
- Multiplication Formula
- Multiplication Using a Number Line
- Multiplication Tables (up to 10)
- How to multiply the numbers?
- Multiplication without regrouping
- Multiplication with regrouping
- Solved Examples
- Tips and Tricks on Multiplication
- Conclusion
- FAQs on Multiplication
What is Multiplication?
Multiplication is a basic operation that adds the same number again and again. It is also known as repeated addition. This is the method to find the total when groups of the same size are given.
For example, 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 is the same as 4 times 2.
2 + 2 + 2 + 2 = 8
So, 2 added 4 times equals 8.
Thus, in a simple way multiplication tells how many times a number is added to itself. The numbers that are multiplied are known as factors and the result is known as the product.
Example: There are 6 baskets with 3 apples in each, which means adding three apples 6 times gives a total of 18 apples.
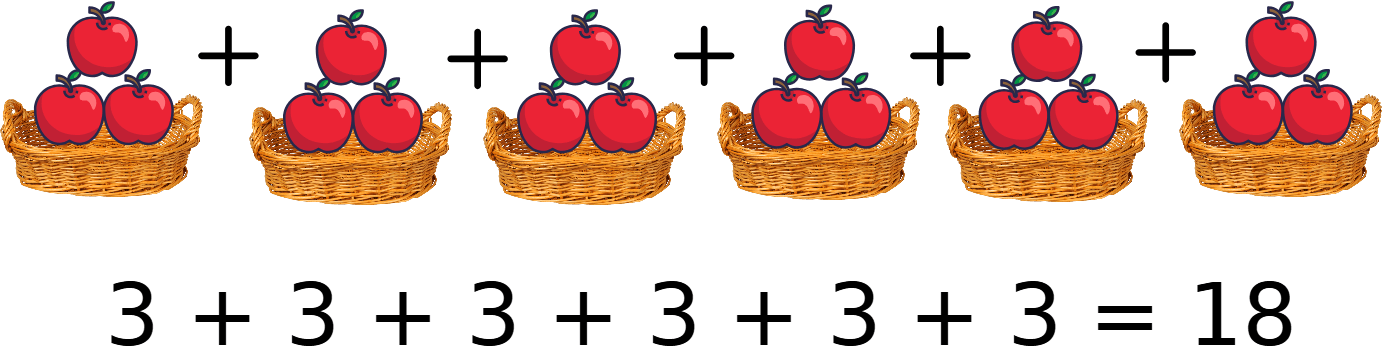
Multiplication Symbol
The symbol that represents multiplication is the cross (x). It is also represented using a dot (.).
Examples:
-
2 x 10 = 20
-
100 x 5 = 500
-
5 . 5 = 25
-
11 . 4 = 44
Multiplication Formula
The formula for multiplication is expressed as follows:
![]()
Where,
-
Multiplicand is the first factor.
-
Multiplier is the second factor.
-
The product is the result of multiplying both factors.
Example:
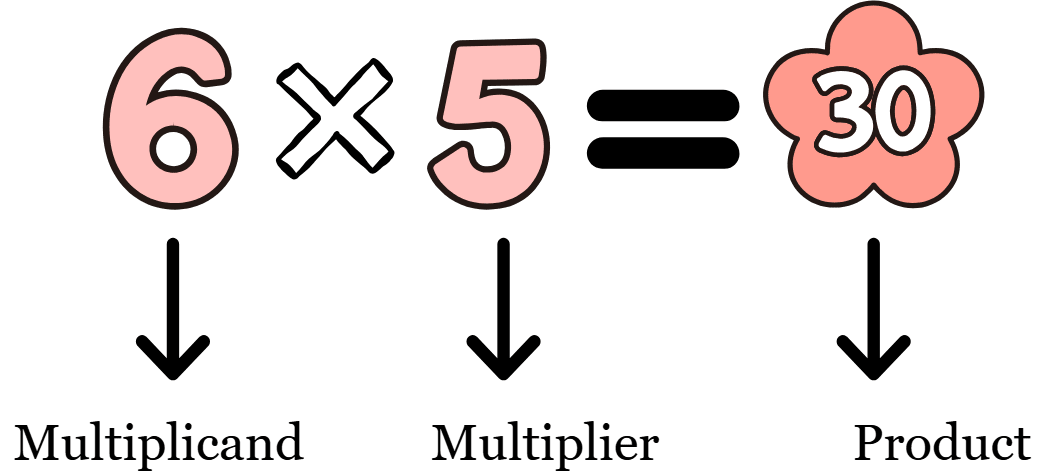
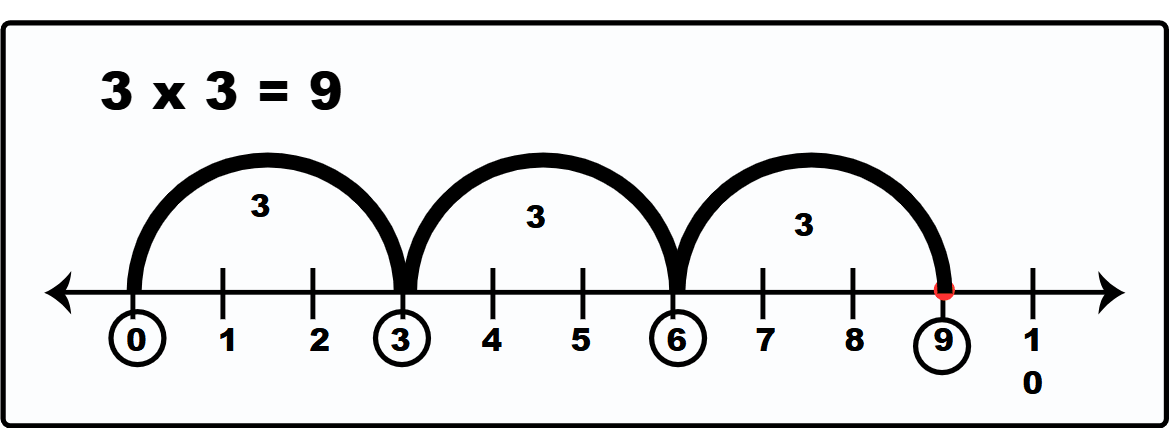
Multiplication Using Number Line
Multiplying using a number line is nothing but performing multiplication operations on a given set of numbers with the help of a number line. A number line is a visual representation of numbers using a straight line. As we know that multiplication and repeated addition are the same, to multiply on the number line, we start from zero and jump to the right side of the number line for a given number of times.
For example: Multiply 3 x 3 using the number line.
Steps for multiplying using the number line are as follows:
-
Start from 0.
-
Make 3 jumps for 3 units each.
-
We will end up at 9, which is a product of 3 and 3.
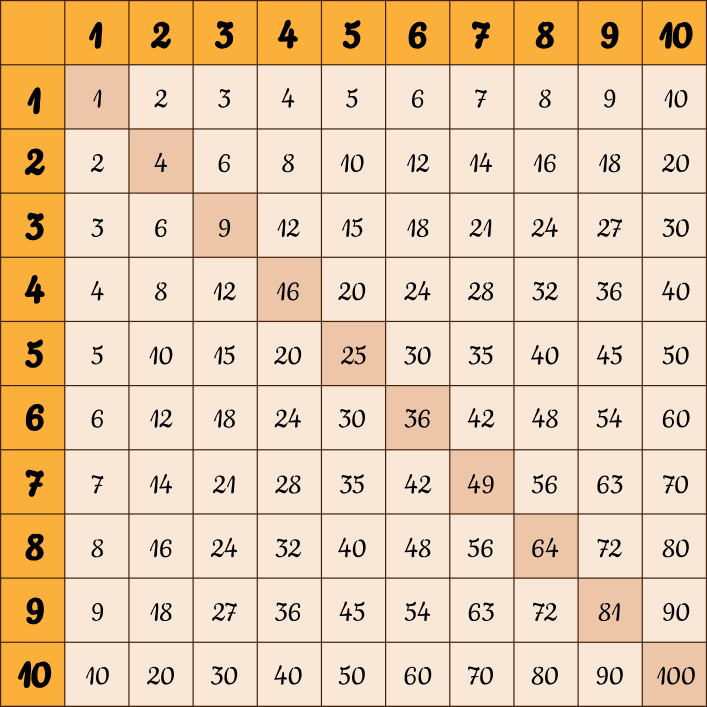
Multiplication Tables (up to 10)
Multiplication tables are essential for efficient calculation. The table below shows a multiplication table or times table from 1 to 10. This table helps to perform multiplication easily and quickly.
How to multiply the numbers?
Multiplying one-digit numbers with one-digit numbers is simpler using the multiplication tables. But how will you multiply larger numbers? We arrange the numbers in a column and do the calculation. There are two methods to multiply based on the given factors.
-
Multiplication without regrouping
-
Multiplication with regrouping
Let us learn these methods with the examples.
Multiplication without regrouping
Multiplication without regrouping is the basic level of understanding how to multiply numbers. This basically involves multiplying directly, which does not require carry-over to the next highest place value.
Steps involved in multiplication without regrouping are as follows:
-
Arrange the given numbers in a column according to the place value.
-
Multiply the ones column and write down the result under the ones column.
-
Multiply the tens column and write down the result under the tens column.
-
Multiply the hundreds column and write down the result under the same column.
-
This process continues for a number of digits in the number.
-
The final number is the product of the given numbers.
Example: Multiply 4234 x 2
Solution:
-
Arrange the given numbers in a column according to the place value.
-
Multiply the ones column i.e., 4 and 2 which results as 8 and write down the 8 under ones column.
-
Multiply the tens column, i.e., 3 and 2, which results in 6 and write down the 6 under the tens column.
-
Multiply the hundreds column, i.e., 2 and 2, which results in 4 and write down the 4 under the hundreds column.
-
Multiply the thousands column, i.e., 4 and 2, which results in 8 and write down the 8 under the thousands column.
-
Therefore, the product of 4234 and 2 is 8468.
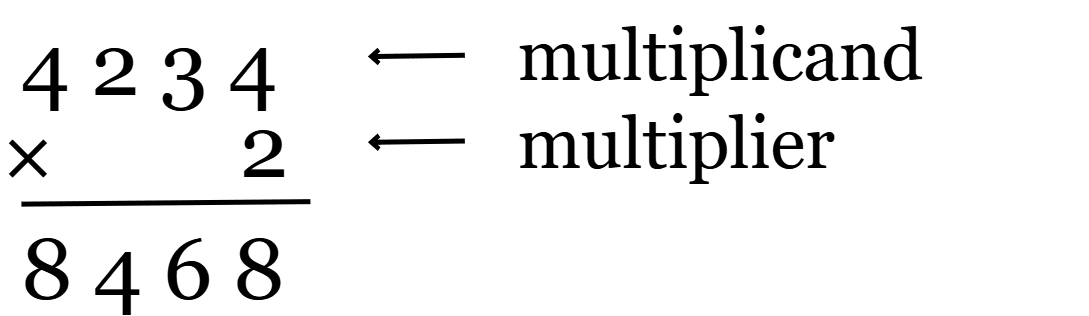
Multiplication with regrouping
Multiplication with regrouping is used when there is a need for carry-over to the next highest place value. If there are large numbers, this method is used. Times tables help to reduce time while multiplying large numbers.
Steps involved in multiplication with regrouping are as follows:
-
Arrange the given numbers in a column according to the place value.
-
Multiply one column and if the product is a 2-digit number, then write ones digit of the product under ones column and carry the tens digit to the tens place.
-
Multiply the tens column and add the product with the carried number of ones place product. If again the sum is a 2-digit number, then write ones digit under the tens column and carry the tens digit to the hundreds place.
-
Multiply hundreds columns and add the product with a carried number of tens place product. If again the sum is a 2-digit number, then write ones digit under the hundreds column and carry the tens digit to the thousands place.
-
If the product of the last highest place value is two digit, then write as it is under that place value column.
Example: 269 x 2
Solution:
-
Arrange the given numbers in a column according to the place value.
-
Multiply ones column, i.e, 9 and 2 and the product is 18, now write 8 under ones column and carry 1 to the tens place.
-
Multiply the tens column, i.e, 6 and 2, which results as 12 and add the product with the carried number of ones place product (12 + 1 = 13). Again, the sum is a 2-digit number (13), then write 3 under the tens column and carry 1 to the hundreds place.
-
Multiply hundreds columns, i.e., 2 and 2, which results in 4 and add the product with the carried number of tens place product (4 + 1 = 5). The sum is 5, then written under the hundreds column.

Solved Examples
Let us learn with some examples to understand the concepts discussed.
Example 1: 12 x 8
Solution:
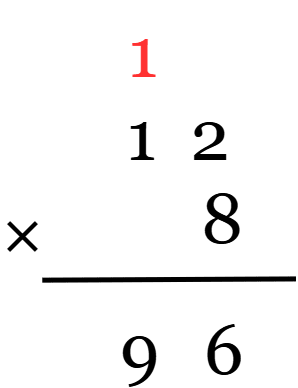
Example 2: A bakery sells 24 cakes per day. How many cakes do they sell in 12 days?
Solution:
Given,
A bakery sells 24 cakes per day.
We need to find the total number of cakes sold in 12 days.
24 x 12 = ?
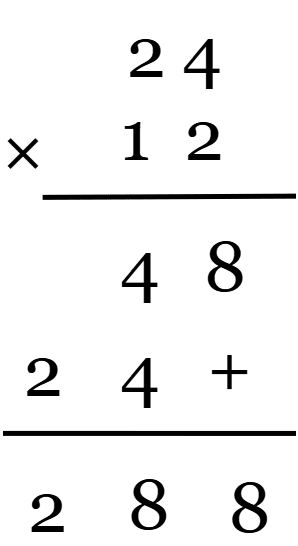
Therefore, 288 cups were sold in 12 days.
Example 3: Multiply 4325 by 25.
Solution:

Therefore, 4325 x 25 = 1,08,125
Tips and Tricks on Multiplication
The tips and tricks that make multiplication easier and faster are as follows:
-
While multiplying the order of numbers does not matter. One can choose the order that is comfortable and easy to multiply.
-
Use multiplication tables and remember tables up to 20.
-
Multiplying 10, 100 and 1000 just adds zeros to the given number. For example: 2345 x 10 = 23450, 5768 x 100 = 576800 and 456 x 1000 = 456000.
-
If there are three numbers to multiply, first multiply the small numbers and then multiply the product by the large numbers.
-
While multiplying 2-digit, 3-digit, or 4-digit numbers better to split the multiplicand based on place values and multiply with the multiplier and then add all the products.
(For example: 35 x 5 = (30 + 5) x 5 = (30 x 5) + (5 x 5) = 150 + 25 = 175)
Conclusion
Multiplication is a basic mathematical operation that is necessary in our daily life. By understanding the concept, practicing frequently and using the tips and tricks, one can tackle multiplication problems and continue the journey in exploring mathematics. Make use of practice sessions from the page to understand the concept. Whenever you feel it is difficult to solve multiplication problems, don't forget to revisit the page and revise the concept.
FAQs on Multiplication
Q1. What is Multiplication?
Answer: Multiplication is a method of calculating the product of two or more numbers. It is also known as repeated addition. Basically, adding the same number again and again is multiplication. The numbers that are multiplied are factors and the result obtained is the product. The parts of multiplication are multiplicand, multiplier and product. Where, multiplicand is the first factor, the multiplier is the second factor and the product is the result after multiplication.
Q2. What is the formula used to perform the multiplication?
Answer: The formula used to perform the multiplication is Multiplicand x Multiplier = Product.
For example: 3 (multiplicand) x 2 (multiplier) = 6 (product)
Q3. What are the general methods to perform multiplication?
Answer: There are two types of methods, one is multiplication without regrouping or carry-over and the second is multiplication with regrouping or carry-over.
Q4. Is there any relation between multiplication and addition? Give a reason.
Answer: Yes, multiplication is also known as repeated addition. Adding the same number again and again is nothing but multiplication.
Q5. What is the difference between multiplication and division?
Answer: In multiplication, we combine the equal-sized groups, but in division, we split or separate them into equal groups.
CBSE Schools In Popular Cities
- CBSE Schools in Bangalore
- CBSE Schools in Mumbai
- CBSE Schools in Pune
- CBSE Schools in Hyderabad
- CBSE Schools in Chennai
- CBSE Schools in Gurgaon
- CBSE Schools in Kolkata
- CBSE Schools in Indore
- CBSE Schools in Sonipat
- CBSE Schools in Delhi
- CBSE Schools in Rohtak
- CBSE Schools in Bhopal
- CBSE Schools in Aurangabad
- CBSE Schools in Jabalpur
- CBSE Schools in Jaipur
- CBSE Schools in Jodhpur
- CBSE Schools in Nagpur
- CBSE Schools in Ahmednagar
- CBSE School In Tumkur











