Plant Form and Function
Fun Prep Up:
You have heard about how plants grow, breathe & survive. Imagine you’re a small seed resting deep into the earth. You begin your life as a tiny, nearly undetectable dot, but eventually you reach your limbs to the sun and become something truly wonderful! Plants are like nature’s superheroes, miraculously collaborating to create what we need from sunlight to food, supplying us with oxygen & cleaning the air around us. But how do they do all this? So come with me, and let’s explore the wonderful world of plant form & function!
The Basics of Plant Form: What Does a Plant Look Like?
When we think about plants, we envision stems, leaves and roots. These are the key elements of a plant and have an essential function in keeping it alive & flourishing.
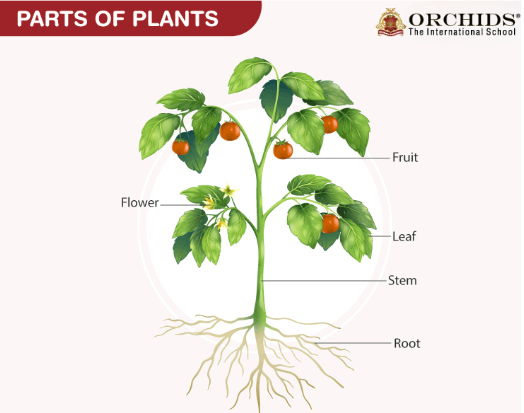
- Roots: Roots hold the plant in the ground and take in water & nutrients from the soil. A plant can’t reach high or draw in what it needs to survive without strong roots.
- Stems: Stems are the plant’s highways, transporting water, nutrients & food to various parts of the plant. They prop up the plant to allow it to absorb as much sunlight as it can.
- Leaves: So, leaves are the food factories of the plant. Leaves use sunlight, water & carbon dioxide to produce food that serves as energy for the plant during a process called photosynthesis.
The Function of Roots: Plant’s Anchor and Nourishment
Roots are not just the underground portion of the plant. They are critical to the plant’s survival. Roots help in several ways:
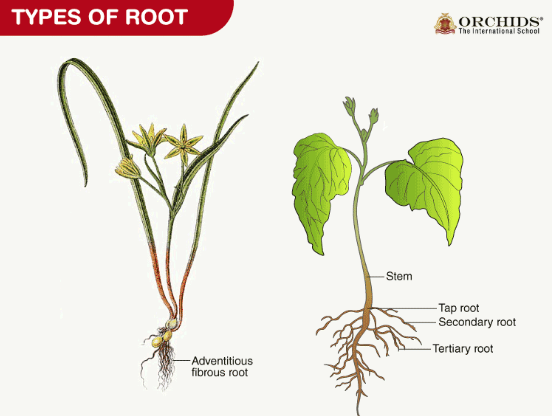
- Anchoring the Plant: Roots Providing Light , Roots not only help keep a plant in one spot, but they also help promote a healthy environment.
- Absorbing Water and Nutrients: Plants absorb water and essential minerals from the soil through tiny root hairs. Without this water & minerals, the plant would not grow.
- Storing Food: Some plants such as carrots & sweet potatoes store food in their roots. This aids the plant to endure cold weather like the winter.
The Role of Stems: The Plants Transport System
A stem connects the roots to the leaves. “Here are two functionalities that it serves:
- Transporting Nutrients and Water: Stems transport water & minerals from the roots to the leaves. They also transport food (glucose) made in the leaves to other parts of the plant.
- Supporting the Plant: Stems keep the plant upright and support leaves & flowers. This allows the plant to reach sunlight, which is essential for photosynthesis.
- Storage: In certain plants, stems serve to store food as well. For instance, cactus plants grow thick stems to store water & live in dry weather.
Leaves: The Food Factories of the Plant
Leaves are truly amazing! They capture light from the sun and through a process known as photosynthesis convert it into food that the plant can utilize to grow & create energy. So what do we know about leaves?
- Photosynthesis: The process by which plants produce their food. Leaves have a substance called chlorophyll in them that grabs sunlight. Chlorophyll, taking in water from the roots & carbon dioxide from the air, converts sunlight into sugar on which plants feed.
- Gas Exchange: In addition, leaves also aid in exchanging gases. Small pores on the leaves, known as stomata, admit carbon dioxide and exhale oxygen. This process is important for both the plant & the environment.
- Transpiration: Transpiration is when water evaporates from the leaves into the atmosphere. It may sound like a waste of water, but this process, called transpiration, actually cools the plant & pulls water up from the roots.
The Flower and Fruit: Reproduction & Survival
Flowers are not just aesthetically pleasing ,they are crucial for the reproduction of plants. When plants germinate, they reproduce, and corn is no exception. Flowers have both male & female components that combine to form seeds, which then develop into new plants.
- Pollination: Pollination allows the pollen of a flower to reach the female part of another flower. Insects, wind or even animals can do this.
- Fruits and Seeds: Fruits that contain seeds often develop from flowers after pollination. These seeds are necessary to grow new plants. Fruit may also serve to protect the seed & disperse it to new locations.
Plant Adaptations: Surviving in Different Environments
Plants are so adaptable, and can grow in environments from the dry desert, to the wet rainforest. Whether it be hot, cold, or damp, they have specific adaptations that allow them to thrive in varying environments.
- Cacti: Cacti are found in hot, dry deserts. They have thick stems that store water. They also have small leaves or no leaves to minimize loss of water.
- Water Plants: Some plants grow in water lilies, for instance. Their leaves have a waxy coating that keeps water from being absorbed into them.
- Tropical Plants: Plants in rainforests have wide broad leaves in order to absorb as much sunlight as possible in the shady forest.
Conclusion
Plants are amazing things that teach us how life can flourish with nature. Every part of a plant plays a specific role from roots to leaves, to stems & flowers that assist with things like growth, survival, and reproduction. Ecosystem Biology Plant structure & function are essential not only for understanding the biological world but also to recognize the significance of plants in our environment.
CBSE Schools In Popular Cities
- CBSE Schools in Bangalore
- CBSE Schools in Mumbai
- CBSE Schools in Pune
- CBSE Schools in Hyderabad
- CBSE Schools in Chennai
- CBSE Schools in Gurgaon
- CBSE Schools in Kolkata
- CBSE Schools in Indore
- CBSE Schools in Sonipat
- CBSE Schools in Delhi
- CBSE Schools in Rohtak
- CBSE Schools in Bhopal
- CBSE Schools in Aurangabad
- CBSE Schools in Jabalpur
- CBSE Schools in Jaipur
- CBSE Schools in Jodhpur
- CBSE Schools in Nagpur
- CBSE Schools in Ahmednagar
- CBSE School In Tumkur











