Composition and Properties of Air [8 Practice Worksheets]
This is a comprehensive lesson plan for teaching Composition and Properties of Air to class 2, 3 and 4. The lesson is designed to make the concept easy and engage students with various activities like quizzes, practice questions and worksheets.
Teachers can use this guide as a reference for delivering the concepts to students.
For parents, there are 8 downloadable practice worksheets that they can use for their kids.
The learning outcomes are as follows:
- Composition of air with different gases
- Properties of air - air contains oxygen, air can move, air has weight etc.
It is evident that air is everywhere though we cannot see it. It is the source of life on this planet. Let's explore the magical world of air, learn what it is made of, and discover it's different properties. But before we discuss those, let us refresh our knowledge on what air is and why do we need it.
What is Air?Air is mostly gas. It is all around us. We can not see it, but we can feel it when air blows as wind. We breath in air which is oxygen and release carbon dioxide. Hence, can say that air is a mixture of gases.
Why Do We Need Air?Air is vital for life and contains oxygen, which we need to breathe and survive. The main reason plants, animals, and humans all need air is different:
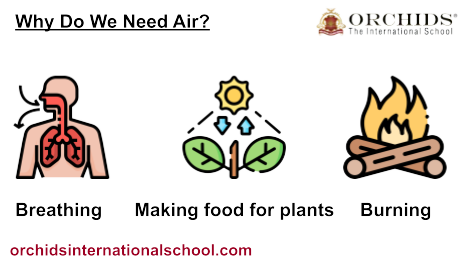
For breathing: Our lungs absorb oxygen from the air to help function properly in our body.
For plants: They use carbon dioxide in the air to produce food by photosynthesis (Learn more on photosynthesis here).
For Energy: Oxygen is crucial for burning fuels that enable the movement of vehicles to promote activities across the globe. Air also acts as a protective shield from the harmful rays of the sun and maintains the perfect temperature for life on Earth.
Test your Understanding:
b) Living organisms would not survive
c) It would always be night time
The Composition of Air
Air is a mixture of gases that comes to envelop the Earth and gives support to life. Though this air appears to be transparent and weightless, it is comprised of several gases; each one plays an important role in maintaining a balance on our planet.
Air is a mixture of various gases. Let’s break it down:
Imagine you have 10 toffees, like the one shown in the image below.
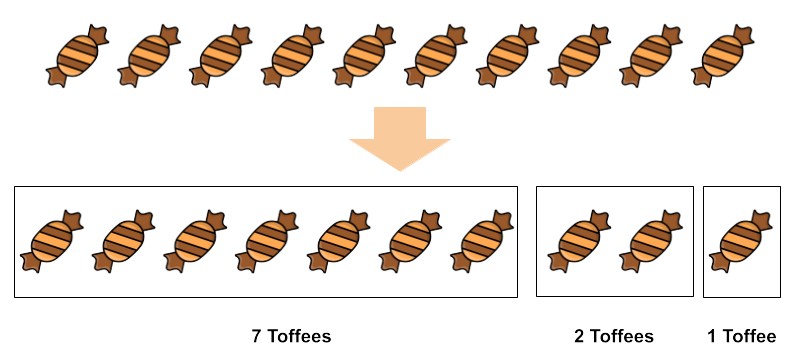
The air around us can also be compared to groups of toffees. Just like the toffees in the image are divided into 3 parts, air is also divided into parts containing different types of gases. The largest part is Nitrogen, the second largest is Oxygen, and the smallest part includes gases like Argon and Carbon Dioxide, along with other things like water vapor, smoke, dust, and germs.
But what are these gases? Let us read more on them.
1. Nitrogen:
- Nitrogen is a colorless, odorless gas (no smell) and is the most common gas in the atmosphere.
- Nitrogen enters the atmosphere through the nitrogen cycle, involving specific living organisms and environmental processes.
- Role in Plant Growth: It is crucial for plant growth as it is used to make fertilizers.
- Importance for Humans - Nitrogen is also an essential part of proteins in the human body.
2. Oxygen:
- Vital for Life: It is essential for respiration (breathing). It is also a supporter of burning.
- Supports Growth: Oxygen helps living beings grow.
- Oxygen is also a component of the ozone layer, which protects life on Earth from harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the Sun.
3. Argon:
- It is a noble gas, which means it doesn’t react easily and is popularly used in light bulbs and welding.
- It is a colorless, tasteless, and odorless gas.
4. Carbon Dioxide:
- Carbon Dioxide is a small component of air.
- It can trap heat and is hence also called a greenhouse gas.
- Plants use carbon dioxide for making food (photosynthesis).
5. Others:
In addition to the above-mentioned gases, air also consists of water vapor, smoke, dust particles, and germs.
Test your Understanding:
1. Which gas is a component of ozone layer that helps in blocking harmful ultraviolet rays from the sun?
a) Nitrogen
b) Oxygen
c) Argon
d) Carbon Dioxide
2. Which gas is used by plants for making food?
a) Oxygen
b) Carbon Dioxide
c) Nitrogen
d) Water Vapour
The Properties of Air
Air is all around us, though we can't see it. It is a mixture of gases that takes up space and has weight. Air can move, creating wind; air is flexible - we can compress or expand it and many more. The properties of air are essential for breathing, flying airplanes, and enjoying activities like balloons and bubbles. Let's look into the image to see the different properties of air.

What are the 10 properties of air?
The 10 properties of air are as follows:
-
Air takes up space: Even though we can’t see it, air fills balloons and our lungs.
-
Air has weight: It pushes down on us, which we call air pressure.
-
Air can move: That’s what creates wind.
-
Air can expand and contract: It grows bigger when heated and shrinks when cooled.
-
Air can flow: It moves around objects like water does.
-
Air has oxygen for life: Essential for breathing.
-
Air is invisible: You can’t see it, but you can feel it.
-
Air can dissolve in water: That’s how fish breathe underwater.
-
Air can carry sound: Without air, we couldn’t hear anything!
-
Air exerts pressure: This helps airplanes fly and keeps objects from collapsing.
Want to know more on properties of air? Check here.
Test your Understanding:
a) Air is visible and has no weight.
2. Which experiment demonstrates that air occupies space?
Facts
Although most gases in the air are safe, some can be harmful. Some examples are:
-
Carbon monoxide: It is a toxic gas emitted from vehicles and burning of substances.
-
Sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides: These gases are emitted from factories, that can cause air pollution.
Quiz
1. What is the most abundant gas in the Earth's atmosphere?
a) Oxygen
b) Carbon dioxide
c) Nitrogen
d) Argon
2. How do we know that air is present around us?
a) We can see it
b) It is visible in pictures
c) We can feel it
d) We can taste it
3. Air is needed for which of the following processes?
a) Breathing
b) Burning
c) Photosynthesis in plants
d) All of the above
4. What happens when air is cooled?
a) Air becomes lighter and moves upward.
b) Air shrinks.
c) Air disappears.
d) Air expands and becomes denser.
5. Which of the following is NOT found in air?
a) Oxygen
b) Nitrogen
c) Water vapor
d) Gold
Practice Worksheets
Click the button to download the worksheets for hands-on practice!
Orchids' Learning Material
Click the button to download the e-book
Things You Have Learnt!
- Air is crucial to support life on Earth. We can live for somedays without food, but we cannot live even for a moment without air.
- Air is made up of gases that are important for breathing, protecting us from harmful rays, and helping plants with photosynthesis.
- Air has many properties, like - air has oxygen for life, air can move, air can carry sound etc.
CBSE Schools In Popular Cities
- CBSE Schools in Bangalore
- CBSE Schools in Mumbai
- CBSE Schools in Pune
- CBSE Schools in Hyderabad
- CBSE Schools in Chennai
- CBSE Schools in Gurgaon
- CBSE Schools in Kolkata
- CBSE Schools in Indore
- CBSE Schools in Sonipat
- CBSE Schools in Delhi
- CBSE Schools in Rohtak
- CBSE Schools in Bhopal
- CBSE Schools in Aurangabad
- CBSE Schools in Jabalpur
- CBSE Schools in Jaipur
- CBSE Schools in Jodhpur
- CBSE Schools in Nagpur
- CBSE Schools in Ahmednagar
- CBSE School In Tumkur











