Sense Organs
1) How Does the Retina of Our Eye Help in the Identification of Colours?
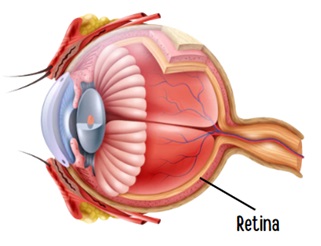
- The retina is a specific place in our eye where image formation takes place.
- The membrane of the retina has two types of cells—rods and cones.
- The rod cells in the retina respond to the intensity of light, and the cone cells to the colours of light.
- Hence, the electrical impulses generated as a response of cone cells help us identify the colours.
2) How Do the Eyes Control the Entry of Light?
- The light entering the eye is controlled by the iris and pupil.
- The size of the pupil is controlled by the muscles of the iris.
- When the intensity of light is high, the pupil contracts, dilating when light intensity is dim.
3) What Is ‘Cataract’?
- A cataract is an eye disorder where the vision becomes blurry because the lens in the eye turns cloudy.
- It generally occurs due to old age.
4) What Is Blind Spot? Why Is No Vision Possible at the Blind Spot?
The blind spot is where the optic nerve and retina of the eye unite. At this point, there are no light-sensitive cells which are necessary for vision.
5) What Do You Understand by a Range of Vision? What Is the Range of Vision of the Human Eye?
- The range of distance for which the objects are clearly visible is called the range of vision of the human eye. It is 25 cm to infinity for the human eye.
- It means that an object is visible to us from close up when it is at a distance of 25 cm from our eye. And we can see objects from an infinite distance.
6) What Helps To Retain the Spherical Shape of Our Eyeballs?
There is a thick liquid called vitreous humour present in our eyeballs. It helps to retain the spherical shape of our eyeballs.
7) Name the Smallest Bone in the Human Body. Where Is It Found?
The middle ear comprises three bones—stapes, incus and malleus—called ossicles.
The stapes is the smallest bone among the ossicles and the smallest bone in the human body.

8) What Is the Function of Ear Wax?
Ear wax is a thick solid substance found in our ear canal. Its functions are as follows—
- To retain moisture and prevent any infections in the ear.
- Prevent dust or insects from entering the ear.
9) The Nose and Ears Never Stop Growing. Comment.
After puberty, our body stops growing. But with age, the cartilage (soft bones in our ears and nose) starts losing its rigidity. It makes ears and nose lose, and due to gravity, they start appearing to sag.
10) Where Are the Thickest and Thinnest Skin Patches Located in the Human Body?
The thickest skin patch is found on the feet, and the thinnest skin patch is on our eyelids.
11) How Does Skin Help in Body Temperature Regulation?
- The skin in our bodies contains blood vessels.
- When the body's temperature rises, the blood vessels dilate to lose the extra heat. It happens with the extra volume of blood flowing through the vessels.
- When our body is cool, the blood vessels get narrowed, which limits the amount of blood flowing. Hence, the body heat gets retained in the body.
12) How Do We Develop a New Outer Layer of Skin on a Wound or a Scratch?
- Our skin cells are capable of making new cells. These new cells combine to create a new layer of skin over the wound or scratch.
- This process starts after the formation of a clot. The time required for developing a new layer of skin depends on the type of injury.
CBSE Schools In Popular Cities
- CBSE Schools in Bangalore
- CBSE Schools in Mumbai
- CBSE Schools in Pune
- CBSE Schools in Hyderabad
- CBSE Schools in Chennai
- CBSE Schools in Gurgaon
- CBSE Schools in Kolkata
- CBSE Schools in Indore
- CBSE Schools in Sonipat
- CBSE Schools in Delhi
- CBSE Schools in Rohtak
- CBSE Schools in Bhopal
- CBSE Schools in Aurangabad
- CBSE Schools in Jabalpur
- CBSE Schools in Jaipur
- CBSE Schools in Jodhpur
- CBSE Schools in Nagpur
- CBSE Schools in Ahmednagar
- CBSE School In Tumkur











