Soil
What is Soil?
Soil is one of the most precious resources of the Earth. It is a complex blend of minerals, organic matter, air and water, which lies on the surface of the planet. Soil is the source of the food that plants make, and plants are the vital source of food for all other life on the planet. planting a small flower in your backyard or cultivating a giant tree in the woods, soil is the foundation. Without it, we wouldn’t have any of the trees, flowers, vegetables or fruits that we enjoy every day.”
Soil isn't just dirt! It’s rife with little organisms — bugs, worms, microbes — that help break down materials and create fertile ground for plants to flourish.
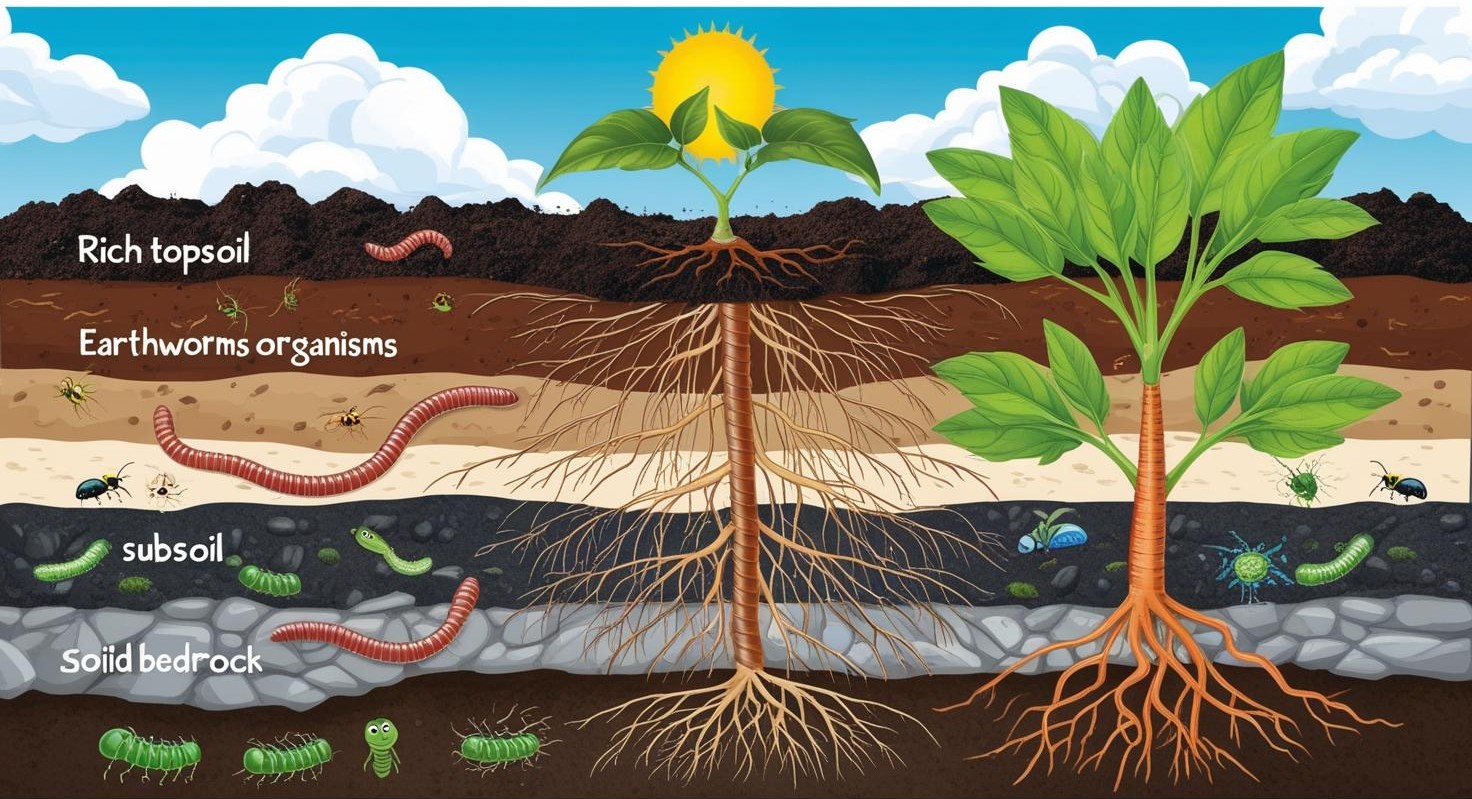
Soil plays a vital role in:
- Plant Growth – It Not only helps the plants grow, it also supplies them with nutrients and water.
- Habitat for Organisms – Soil is home to several microorganisms and insects that contribute towards decomposing and making the soil fertile.
- Water Storage and Filtration – Soil absorbs and retains rain water, thereby preventing floods and preserving subterranean water levels.
- Agriculture and Construction – Now let’s look at some more uses of soil Agriculture and Construction – Soil is the basis for agriculture and construction (houses, roads, etc.).
As soil is a valuable resource, it should be kept safe from erosion and pollution. Soil is the ultimate resource, and soil conservation practices help preserve that due diligence for future use.
Types of Soil
Soil is classified into types according to texture, water-holding capacity and composition. The main types of soil are:
1. Sandy Soil
Sandy soil has large sand grains and very little clay and silt. The large spaces between particles mean that it has a rough texture and does not retain water very well.
Characteristics:
- Light and dry
- Poor in nutrients
- Does not hold water well
- Good for drainage
Uses:
- Ideal for Cultivation of Carrots, Potatoes, and Peanuts
- So it is used in the making of concrete and in construction
- Aids garden drainage
2. Clayey Soil
Contains tightly packed fine particles. It can hold a lot of water but drains very slowly.
Characteristics:
- Heavy and sticky when wet
- Holds water for a long time
- Rich in nutrients
- Becomes hard when dry
Uses:
- Good for crops like rice, sugarcane, and wheat
- Used in making bricks, pottery, and tiles
- Suitable for making ponds and reservoirs because it retains water well
3. Loamy Soil
The best soil for plant growth is loamy soil which means a combination of sand, silt and clay. It holds good water and drainage properties.
Characteristics:
- Soft and crumbly texture
- Holds water and nutrients well
- Contains a good amount of humus (organic matter)
- Best soil for farming
Uses:
- Ideal for growing vegetables, fruits, and grains
- Used in gardening and landscaping
- Helps in maintaining soil fertility
4. Silt Soil
Silt soil is made of fine particles larger than clay and smaller than sand. It is fine and retains moisture better than sandy loam.
Characteristics:
- Smooth and soft
- Holds moisture well
- Rich in nutrients
- Can be easily compacted
Uses:
- Suitable for farming and gardening
- Used in riverbanks to prevent erosion
- Helps in improving soil fertility when mixed with sand or clay
5. Peaty Soil
Peat soil has high water content and lots of organic matter. It comes from wetland locations, and its dark color comes from decomposed plant material.

Characteristics:
- Dark in color
- Holds a lot of moisture
- Contains high organic matter
- Can be acidic
Uses:
- Used in gardening and agriculture when treated properly
- Helps in soil improvement by increasing organic content
- Used as a fuel source in some countries
6. Chalky Soil
Chalky soil consists of calcium carbonate and limestone. It is not conducive to many types of plants and is alkaline in nature.
Characteristics:
- Light-colored and dry
- Does not hold water well
- Alkaline in nature
- May contain stones
Uses:
- Suitable for specific plants like lavender and spinach
- Used in construction and cement production
- Helps in improving acidic soils when mixed with other types
Key Points to Remember
-
Soil supports life! It’s what plants — for food and oxygen — are made of.
-
Plants require different soils. Some like sandy soil, and others like loamy or clay-rich soils.
-
Healthy soil = happy plants! Good soil yields good plants.
-
Soil can be improved! You can add compost and other organic matter to your soil to enhance its vitality.
Soil is a living system and just like us, it requires care and attention. With the right type of soil you can ensure that your plants grow strong and healthy!
Conclusion
Soil is one of Earth’s most crucial resources—and nearly a million times more than dirt! It is the basis for all life by enabling plant growth and providing a wholesome environment for animals and humans. Understanding the different types of soil and how to care for them will make you a better gardener and keep the planet healthy.
As they say – Healthy soil equals healthy plants and healthy plants equal a healthier world!
CBSE Schools In Popular Cities
- CBSE Schools in Bangalore
- CBSE Schools in Mumbai
- CBSE Schools in Pune
- CBSE Schools in Hyderabad
- CBSE Schools in Chennai
- CBSE Schools in Gurgaon
- CBSE Schools in Kolkata
- CBSE Schools in Indore
- CBSE Schools in Sonipat
- CBSE Schools in Delhi
- CBSE Schools in Rohtak
- CBSE Schools in Bhopal
- CBSE Schools in Aurangabad
- CBSE Schools in Jabalpur
- CBSE Schools in Jaipur
- CBSE Schools in Jodhpur
- CBSE Schools in Nagpur
- CBSE Schools in Ahmednagar
- CBSE School In Tumkur











