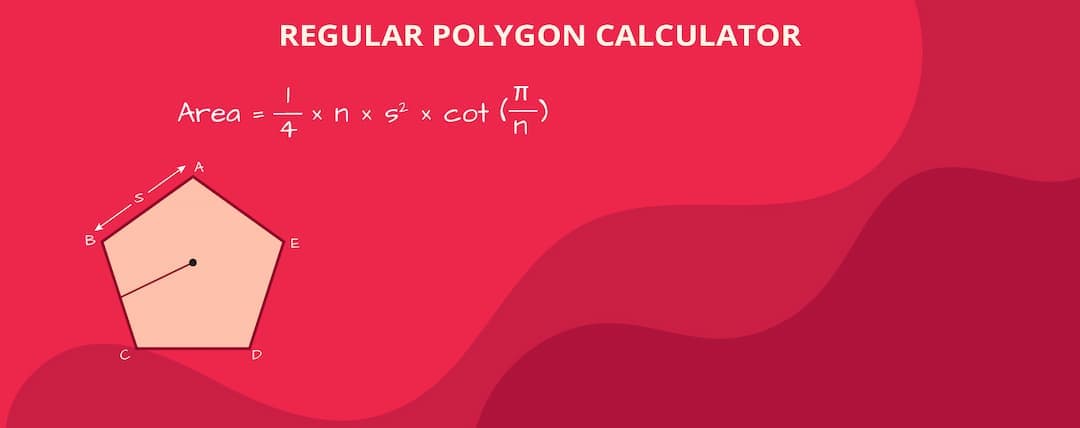
Admissions Open for
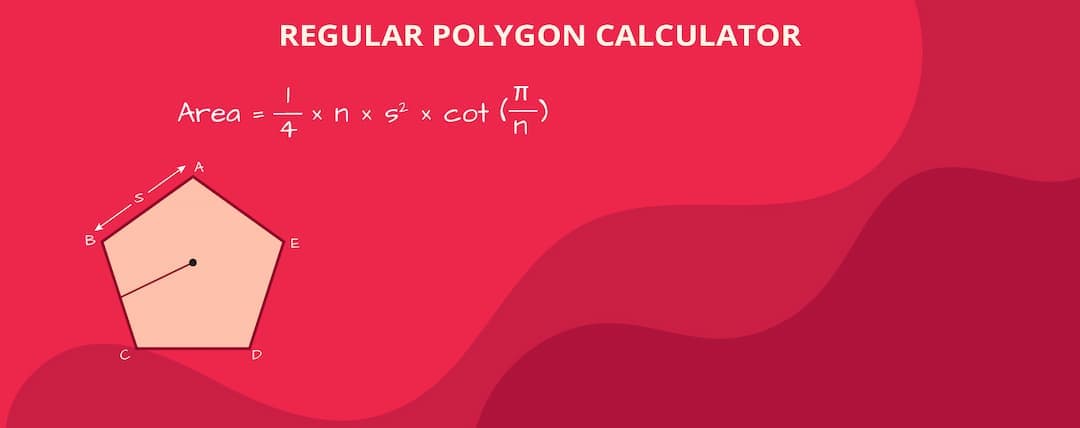
Admissions Open for
Regular Polygon Area Calculator
The area of a regular polygon is the measure of the space enclosed within its boundaries. A regular polygon is a shape with equal sides and angles. Calculating its area involves specific formulas based on the number of sides it possesses.
How to Use the Calculator ?
Enter the number of sides (n) of the regular polygon.
Enter the length of each side (s) of the regular polygon.
Click on the
When should I use this calculator ?
This calculator is helpful whenever you need to quickly determine the area of a regular polygon without going through extensive manual calculations.
What is the formula for the area of a regular polygon?
The formula for finding the area of a regular polygon is:
n = number of sides
s = length of each side
π = Pi (approximately 3.14159)
Can the calculator find the area for irregular polygons?
No, this calculator is specifically designed for regular polygons with equal sides and angles.
Is there a limit to the number of sides this calculator can handle?
The calculator can compute the area for regular polygons with up to 10 sides, including the option for n sides.
Examples:
Let's find the area of a regular pentagon (5 sides) with each side measuring 6 units.
Solution:
Number of sides (n) = 5
Length of each side (s)= 6 units
Using the formula:
Area = 647.373. units
Consider a regular hexagon (6 sides) with a side length of 8 units.
Solution:
Number of sides (n) = 6
Length of each side (s)= 8 units
Using the formula:
Area = 4661.6656. units
Other polygons include pentagon, hexagon, heptagon, and so on as given the table below.
| Polygon(s) | Name | Number of Sides |
|---|---|---|
| 3-sided | Triangle | 3 |
| 4-sided | Square | 4 |
| 5-sided | Pentagon | 5 |
| 6-sided | Hexagon | 6 |
| 7-sided | Heptagon | 7 |
| 8-sided | Octagon | 8 |
| 9-sided | Nonagon | 9 |
| 10-sided | Decagon | 10 |
| n-sided | n-gon | n |
Frequently Asked Questions
Regular polygons have equal sides and angles, while irregular polygons lack uniformity in their sides or angles.
Understanding the area of a regular polygon is crucial in various fields such as geometry, architecture, and design, where precise measurements and calculations are required.
The formula is derived by dividing the polygon into congruent triangles, determining the area of one triangle, and then multiplying it by the total number of sides.
The tangent function is used to calculate the area based on the number of sides in the polygon. It's an essential part of the formula that accounts for the shape and size of the polygon.
Popular Searches
- NCERT Solutions for Class 1 subjects
- NCERT Solutions for Class 2 subjects
- NCERT Solutions for Class 3 subjects
- NCERT Solutions for Class 4 subjects
- NCERT Solutions for Class 5 subjects
- CBSE School In Aurangabad
- CBSE Schools In Bangalore
- CBSE School In Bhopal
- CBSE Schools In Chennai
- CBSE Schools In Delhi
- Best CBSE Schools In Gurgaon
- CBSE School In Hyderabad
- CBSE School In Indore
- CBSE School In Jabalpur
- CBSE Schools In Jaipur
- CBSE Schools In Kolkata
- CBSE Schools In Mumbai
- CBSE Schools In Nagpur
- CBSE Schools In Pune
- Top CBSE School In Rohtak
- Best CBSE Schools In Sonipat











