Admissions Open for

Admissions Open for
Wavelength Calculator
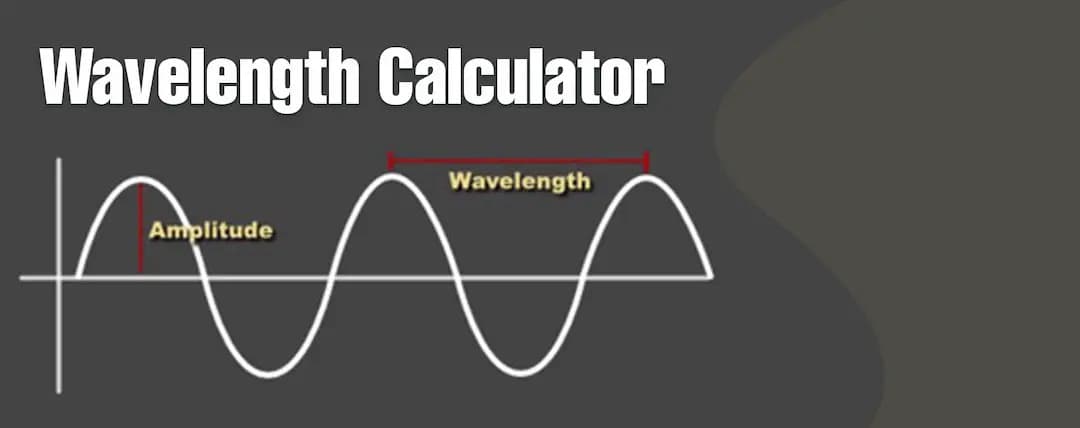
What is Wavelength?
The distance between two waves can be referred to as wavelength. It can be calculated as the distance between two points of a wave.
What is Wavelength?
The distance between two waves can be referred to as wavelength. It can be calculated as the distance between two points of a wave.
Formula To Calculate Wavelength
Wavelength(λ) = Velocity(v) / Frequency(ƒ)
Here,
λ representes wavelength in meters (m),
v representes velocity in meters per second (m/s),
f representes frequency which is represented in hertz (Hz).

How to Calculate Wavelength?
To calculate the wavelength, you need the frequency and velocity of the wave.
- Step 1: Take the formula for calculating the wavelength.
- Step 2: Place the wavelength values, i.e. frequency and velocity, in the wavelength equation λ = v/f.
- Step 3: Lastly, calculate the result.
Example:
Frequency = 120 Hz, velocity = 20,000 m/s, find the wavelength.
Solution:
- λ = 20,000/120
- λ = 166.66 m.
- The wavelength is 166.66 m.
How to Use the Wavelength Calculator ?
- Write the velocity or frequency in the given space.
- Click on the "Calculate" option to get the result.
- You can see the result on the screen.
Frequently Asked Questions
To calculate the wavelength from frequency, you need to divide the velocity by the frequency.
Example:
Find out the wavelength of a wave with a velocity of 40 m/s and a frequency of 12 kHz.
Solution:
λ = v/f
λ = 40/12
λ = 3.33 m.
The wavelength of a wave can be calculated by dividing the speed of the wave by its frequency. Frequency can be referred to the time taken by a complete wave to cross the same point.
Wavelength and frequency are inversely proportional to each other. If a wavelength is more, the frequency is less, and vice versa.
The symbol λ is lambda which is a Greek letter. This symbol denotes wavelength.
Yes, if the frequency of a wave is higher, the wavelength will be shorter, and shorter frequencies mean longer wavelength.
Popular Searches
- NCERT Solutions for Class 1 subjects
- NCERT Solutions for Class 2 subjects
- NCERT Solutions for Class 3 subjects
- NCERT Solutions for Class 4 subjects
- NCERT Solutions for Class 5 subjects
- CBSE School In Aurangabad
- CBSE Schools In Bangalore
- CBSE School In Bhopal
- CBSE Schools In Chennai
- CBSE Schools In Delhi
- Best CBSE Schools In Gurgaon
- CBSE School In Hyderabad
- CBSE School In Indore
- CBSE School In Jabalpur
- CBSE Schools In Jaipur
- CBSE Schools In Kolkata
- CBSE Schools In Mumbai
- CBSE Schools In Nagpur
- CBSE Schools In Pune
- Top CBSE School In Rohtak
- Best CBSE Schools In Sonipat











