Aluminium Bromide Formula
The formula for Aluminium Bromide is AlBr3. It is also known as the Cupric Chloride formula. In this compound, Aluminium has a +3 oxidation state and Bromide has a -1 oxidation state.
Aluminium Bromide is commonly found in two types.
Anhydrous Aluminum Bromide: Colorless to white solid, this compound acts as a catalyst for many chemical reactions. The formula for it is AlBr3.
Hydrated Aluminium Bromide: In this, water molecules are attached to the Aluminum . For instance, one observes that AlBr3⋅6H2O represents Aluminium Bromide hexahydrate.
Aluminum Bromide Formula Structure
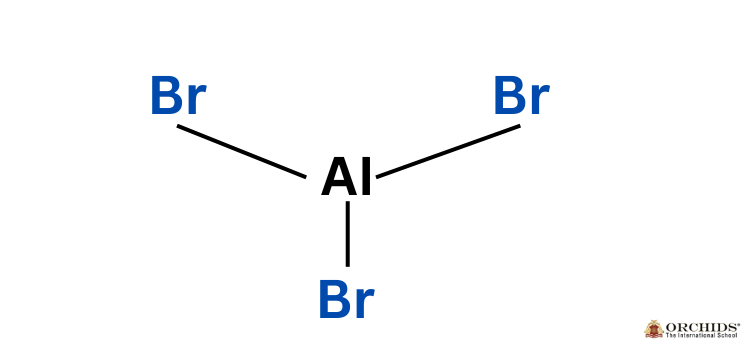
Physical properties
Appearance: It is a white or colorless crystalline solid.
Melting and boiling points: The melting point and boiling point of Aluminum Bromide is 97.5°C and 255°C respectively.
Hexahydrate: Aluminum Bromide hexahydrate is a high water-soluble crystalline Aluminum source for uses compatible with Bromides and lower (acidic) pH.
Solubility: It is highly soluble in water, and forms an acidic solution due to hydration.
Hygroscopicity: It has a high hygroscopicity property, i.e. it actively absorbs moisture from the air, which leads to the formation of the hydrated form.
Physical state: At room temperature anhydrous Aluminium Bromide is found in the solid state, but on heating transforms into gas, this method is usable in some chemical processes.
Chemical properties
Hydrolysis: When reacted with water Aluminium Bromide produces Aluminium Hydroxide and Hydrobromic acid. The reaction is
AlBr3+3H2O→Al(OH)3+3HBr
Formation of complexes: Aluminium Bromide is a Lewis acid and can form complexes with Lewis bases.
It can react with ethers or other electron-donating compounds and forms coordination complexes.
Reaction with bases: Aluminium Bromide reacts with strong bases like Sodium Hydroxide, to form Aluminium Hydroxide and a Bromide salt.
AlBr3+3NaOH→Al(OH)3+3NaBr
Reaction with organic compounds/ Friedel-Crafts reactions: Aluminium Bromide is a catalyst in Friedel-Crafts alkylation and acylation reactions. results in the formation of carbon-carbon bonds by acting as a Lewis acid, promoting the formation of carbocation intermediates.
Sublimation process: On heating Aluminium Bromide hexahydrate. directly went to a gas state from a solid state without passing through a liquid phase. It is called a sublimation reaction. It can be useful for purification and handling in certain chemical processes.
Chlorination: It also can react with non-metal like Chlorine gas to form Aluminium Chloride and Bromine.
2AlBr3+3Cl2→2AlCl3+3Br2
Stability: Anhydrous Aluminium Bromide is reasonably stable in dry conditions. It is, however, highly hygroscopic and absorbs moisture from the atmosphere, promptly turning into its hexahydrate. The hexahydrate, on the other hand, is less stable and decomposes in water.
Application:
Aluminium Bromide has several unique properties, hence use in various fields.
Catalysis in organic synthesis: Aluminium Bromide is an important catalyst in Friedel-Crafts alkylation and acylation reactions. These reactions are useful in the synthesis of various organic compounds, including pharmaceuticals, fragrances, and dyes.
Preparation of Aluminium Chloride: In the reaction of Aluminium Bromide and chlorine gas, Aluminium Chloride is produced, which is another important catalyst in organic chemistry
2AlBr3+3Cl2→2AlCl3+3Br2
Chemical reactions: It is utilized in research studies to examine its properties and reactivity. It serves as a model compound in the study of behaviors of Aluminium halides and their interactions with other substances.
Polymerization: It can act as a catalyst or co-catalyst in several polymerization processes; initiation of polymer chains is possible because the rate of reaction between monomers increases with its use.
Bromine preparation::Aluminum Bromide can also be utilized in the preparation of Bromine from Bromine-containing compounds using displacement reactions.
Industrial organic synthesis::Industrial applications of Aluminum Bromide make the chemical useful for organic syntheses in the manufacturing of various chemicals like specialty and fine chemicals.
Laboratory reagent: It is utilized in the laboratory as a reagent due to its tendencies toward the formation of complexes, and the participation of catalysis for both analytical and synthetic issues.
Though useful in several ways, Aluminium Bromide must be handled with caution since it is very corrosive, especially to water, which generates Hydrobromic acid.
Other Related Sections
NCERT Solutions | Sample Papers | CBSE SYLLABUS| Calculators | Converters | Stories For Kids | Poems for Kids| Learning Concepts | Practice Worksheets | Formulas | Blogs | Parent Resource
Admissions Open for
Frequently Asked Questions
The chemical formula for Aluminum Bromide is AlBr₃.
Aluminum Bromide is used primarily as a catalyst in organic synthesis, particularly in the bromination of aromatic compounds. It also has applications in the production of other chemicals and in certain types of chemical research.
CBSE Schools In Popular Cities
- CBSE Schools in Bangalore
- CBSE Schools in Mumbai
- CBSE Schools in Pune
- CBSE Schools in Hyderabad
- CBSE Schools in Chennai
- CBSE Schools in Gurgaon
- CBSE Schools in Kolkata
- CBSE Schools in Indore
- CBSE Schools in Sonipat
- CBSE Schools in Delhi
- CBSE Schools in Rohtak
- CBSE Schools in Bhopal
- CBSE Schools in Aurangabad
- CBSE Schools in Jabalpur
- CBSE Schools in Jaipur
- CBSE Schools in Jodhpur
- CBSE Schools in Nagpur
- CBSE Schools in Ahmednagar
- CBSE School In Tumkur











