(a) PCR
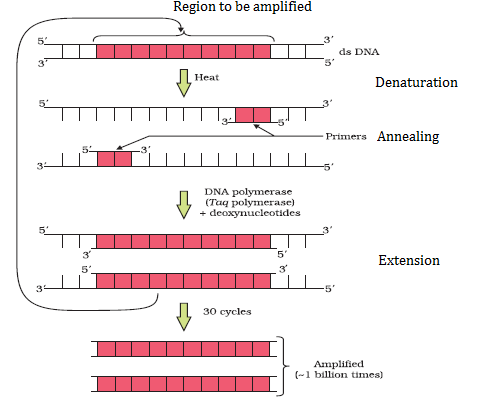
In molecular biology, PCR, or polymerase chain reaction, is a technique to amplify a gene or a fragment of DNA in order to get multiple copies. It is widely used in the gene manipulation process. The phenomenon involves the in vitro synthesis of sequences with the help of a template strand, a primer and a thermostable DNA polymerase enzyme produced by a bacterium known as Thermus aquaticus. The enzyme uses the building blocks deoxynucleotides (dNTPs) in order to extend the primer.
The following are the three steps in PCR:
(i) Initially, the double-stranded DNA molecules are heated to a high temperature to separate the two strands into a single-stranded DNA molecule. This process is referred to as denaturation.
(ii) This DNA molecule is then used as a template strand to synthesise a new strand by the DNA polymerase enzyme. The process is termed annealing, which leads to the replication of the original DNA molecule, and the process is carried out for multiple cycles to obtain multiple copies of the rDNA fragment.
(iii) Primer is extended by Taq DNA polymerase isolated from Thermits aquatics.
(b) Restriction enzymes and DNA
In molecular biology, restriction enzymes are molecular scissors used to cut DNA sequences from a particular site. It has a critical role to play in the gene manipulation process. These enzymes identify a particular six-base pair sequence, referred to as the recognition sequence, and snip the sequence at specific sites. For instance, the recognition site for the ECORI enzyme is given below.
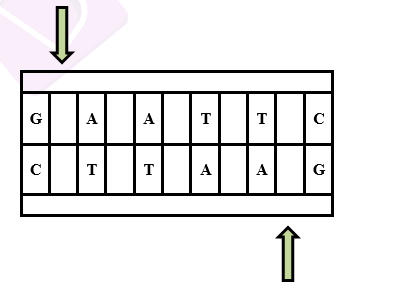
Restriction enzymes are grouped into two types:
(i) Endonuclease – iI is a type of restriction enzyme that cuts within the DNA at specific sites. It serves as a significant tool in genetic engineering. Typically, it is used to make a snip in the sequence to get DNA fragments possessing sticky ends. These ends are later fused by the enzyme DNA ligase.
(ii) Exonuclease – This type of restriction enzyme removes the nucleotides either from the 3’ or 5’ ends of the DNA molecule.
(c) Chitinase
It is a class of enzymes that are used for the degradation of chitin, which forms the main component of the cell wall of fungi. Hence, to isolate the DNA enveloped within the cell membrane of the fungus, the Chitinase enzyme is used to break the cell to release its genetic material.











