Shapes Around Us
The shapes are all around us, from the circular pizza we eat to the rectangular plots we build on. Understanding how to calculate the various measurements of shapes helps us to make sense of the world around us. Whether it is painting walls, planning parties, or constructing houses, we use shapes almost everywhere. Construction, architecture, painting, designing, and planning are some of the primary domains where we use these geometric shapes to our advantage. Let’s learn more about the area and perimeter of various shapes and how to apply them in real life.
Table of Content
- Types of Shapes
- Application of Shapes
- Area of a Shape
- Perimeter of a Shape
- Volume of Shapes
- Sample Problems
- Frequently Asked Questions
Types of Shapes
Geometrical shapes are broadly classified into two major categories- 2D and 3D shapes. We use geometry concepts to work with various 2D as well as 3D shapes like triangles, circles, squares, cubes, cones, etc. The properties of all these geometrical shapes are based on the basic geometrical concepts of line, point, angles, and planes.
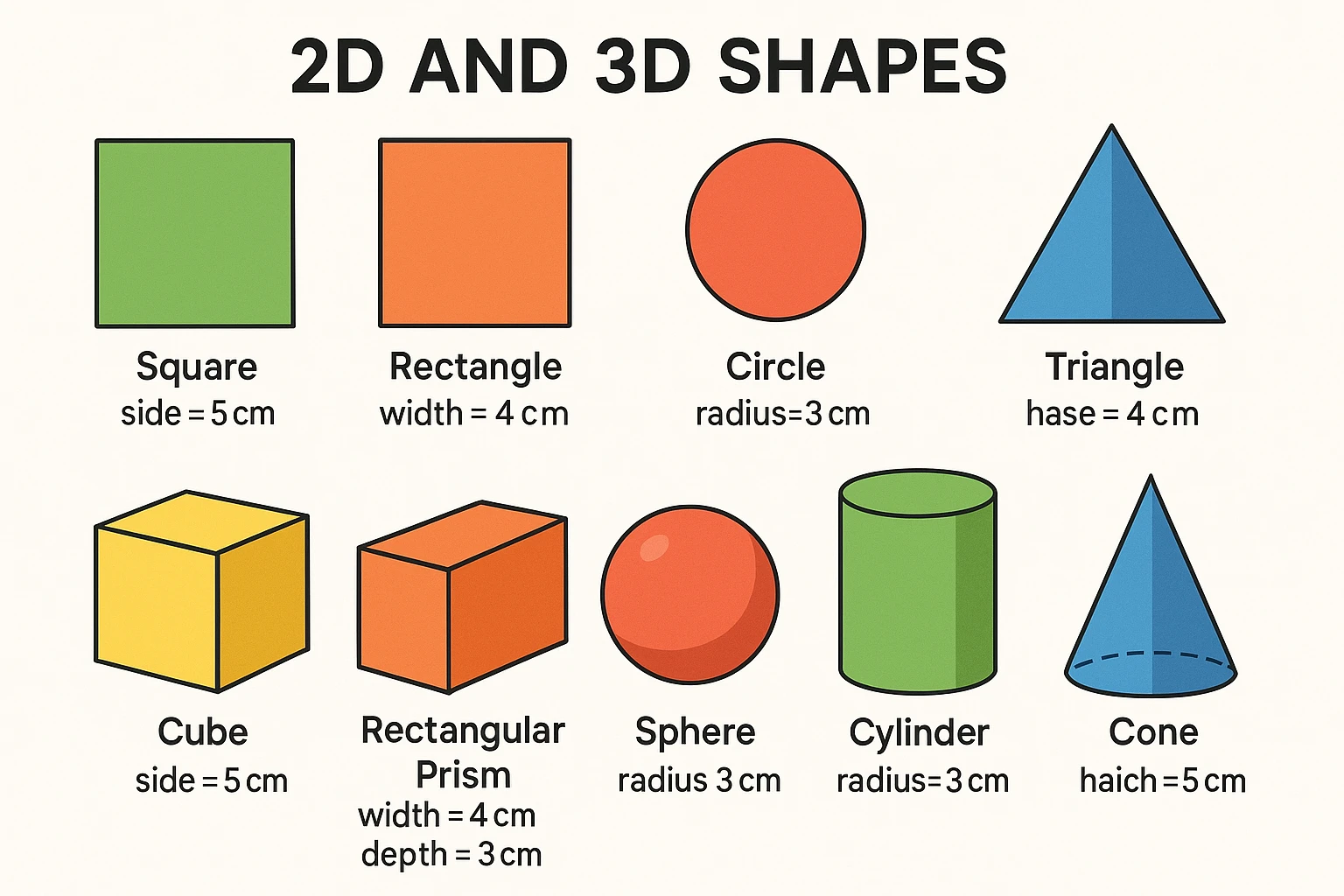
2-D Shapes
|
Shape |
Properties |
Area |
Perimeter |
|
Rectangle |
A four-sided polygon with opposite equal sides & 4 right angles. |
Length X Breadth |
2(Length+Breadth) |
|
Square |
A four-sided polygon with 4 equal sides & 4 right angles. |
Side2 |
4 X side |
|
Triangle |
A triangle is a 3-sided shape with three angles. Depending on the length of their sides, we can classify triangles into three types:
|
½(Base x Height) |
Side-1 + Side-2 + Side-3 |
|
Circle |
A round shape where every point is equidistant from the centre. |
πr² |
2πr |
|
Parallelogram |
A closed shape made of straight lines. For example, a hexagon has 6 sides, and an octagon has 8 sides. |
Base x Height |
2 x (sum of opposite sides) |
3D Shapes
|
Shape |
Properties |
Area |
Volume |
|
Cube |
A solid shape with six equal square faces. |
A=6a² |
V=a3 |
|
Cone |
A 3D shape with a circular base tapering to a single point (apex). |
πr² + πrl |
V = (1/3) * π * r² * height |
|
Cylinder |
3D shape formed by folding a rectangle. E.g., cold drink can |
2πrh+2πr² |
πr²h |
|
Cuboid |
A cube with rectangular faces is a cuboid. |
2 * (lw + wh + lh) |
length × width × height |
Applications of Shapes
Shapes have many applications in real life. The foundation of a house is usually rectangular in shape; by finding the perimeter of the foundation, we can calculate the cost of raising a proper foundation for the house. By finding the area of a rectangular plot, we can estimate the floor area and cost of material used for construction. Gardening is another such example where area and perimeter will help us plant flowerpots all across the perimeter of a garden. Knowing the perimeter & area of a square lawn will help to plant flowerpots all across the perimeter of the lawn and understand the quantity of seeds required to cover the whole lawn. To understand more about the topic and its application, download the area and perimeter of shapes worksheets.
Area of a Shape
The area of a shape is the space enclosed within its boundary. It tells us how much space is occupied by any shape and is usually calculated in square units like square centimetres or square metres. We can use formulas to measure the area of rectangular boxes, square playgrounds, circular pools, and so many other objects using the different formulas of area.
For example, to calculate the area of a rectangular plot, we use the formula Area = Length X Breadth.
Perimeter of a Shape
The perimeter of a shape is the total length of the boundary of a shape. In other words, it is the distance covered along the border of a closed shape. To calculate the perimeter of a shape, we have to add the length of each side. It is measured in linear units like centimetres, meters, or inches. The perimeter of a curved shape like a circle is called a circumference. The formula to calculate the perimeter of a rectangle is Perimeter = 2(Length + Breadth).
Volume of Shapes
The volume of a 3D shape is the amount of space it occupies and is measured in cubic units. Various mathematical formulas are used to find the storage capacity of cylindrical tanks, packaging cost for cubical boxes, etc.
Sample Problems
Sample Problem 1: Find the area and perimeter of a square with side = 6 cm.
Solution: Formula for area of a square: Area = side × side.
Substitute: Area = 6 × 6 = 36.
Area = 36 cm².
Formula for perimeter of a square: Perimeter = 4 × side.
Substitute: Perimeter = 4 × 6 = 24.
Perimeter = 24 cm.
Answer: Area = 36 cm², Perimeter = 24 cm.
Sample Problem 2: Find the area and perimeter of a rectangle with length = 10 cm and width = 4 cm.
Solution:
Area formula: Area = length × width.
Substitute: Area = 10 × 4 = 40.
Area = 40 cm².
Perimeter formula: Perimeter = 2 × (length + width).
First add: length + width = 10 + 4 = 14.
Then multiply: Perimeter = 2 × 14 = 28.
Perimeter = 28 cm.
Answer: Area = 40 cm², Perimeter = 28 cm.
Sample Problem 3: A right triangle has legs 6 cm and 8 cm. Find its area and perimeter.
Solution :
Area formula for triangle: Area = (1/2) × base × height.
Take base = 6 cm and height = 8 cm (they are the two legs).
Area = 1/2 × 6 × 8 = 0.5 × 48 = 24.
Area = 24 cm².
For perimeter, first find the hypotenuse using Pythagoras (because it’s a right triangle):
Hypotenuse = √(6² + 8²) = √(36 + 64) = √100 = 10.
Perimeter = 6 + 8 + 10 = 24.
Perimeter = 24 cm.
Answer: Area = 24 cm², Perimeter = 24 cm.
Sample Problem 4: Find the circumference and area of a circle with radius r = 5 cm. Use π = 3.14.
Solution:
Circumference formula: C = 2 × π × r.
C = 2 × 3.14 × 5.
Compute 2 × 5 = 10 → So C = 10 × 3.14
Circumference = 31.4 cm.
Area formula: Area = π × r².
r² = 5 × 5 = 25.
Area = 3.14 × 25.
Area = 78.05 cm².
Answer: Circumference = 31.4 cm, Area = 78.05 cm².
Frequently Asked Questions on Shapes
1. Name the different types of shapes in geometry.
Answer: Two-dimensional shapes are square, rectangle, triangle, circle, and parallelogram. Three-dimensional shapes are cylinders, cones, cubes, and cuboids.
2. What are 3-dimensional shapes?
Answer: In geometry, a 3-dimensional shape is a solid shape that has three dimensions: length, width, and height. We generally write it as 3D shapes. For example, cylinders, spheres, cuboids, etc.
3. What is the difference between 2D and 3D shapes?
Answer: 2D shapes are flat and only have height and width, while 3D shapes have depth and occupy physical space.
4. What are 2D and 3D shapes?
Answer:
-
2D shapes (two-dimensional) have only length and width. They are flat and cannot be held. Examples: square, circle, triangle.
-
3D shapes (three-dimensional) have length, width, and height (depth). They have volume and occupy space. Examples: cube, sphere, cone.
Admissions Open for
Admissions Open for
CBSE Schools In Popular Cities
- CBSE Schools in Bangalore
- CBSE Schools in Mumbai
- CBSE Schools in Pune
- CBSE Schools in Hyderabad
- CBSE Schools in Chennai
- CBSE Schools in Gurgaon
- CBSE Schools in Kolkata
- CBSE Schools in Indore
- CBSE Schools in Sonipat
- CBSE Schools in Delhi
- CBSE Schools in Rohtak
- CBSE Schools in Bhopal
- CBSE Schools in Aurangabad
- CBSE Schools in Jabalpur
- CBSE Schools in Jaipur
- CBSE Schools in Jodhpur
- CBSE Schools in Nagpur
- CBSE Schools in Ahmednagar
- CBSE School In Tumkur











